
Google Search has become increasingly complex, and it’s no wonder. The informational needs of constantly connected consumers continue to evolve, and search algorithms must adapt to keep up. And do they ever; Google’s algorithms are updated hundreds to thousands of times each year.
Google’s mission is simple: “to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” Google delivers on that mission in a world where 59% of shoppers use Google to search and compare their options before buying online or in-store.
Today, consumers use search on their mobile and desktop devices, from connected devices and vehicles, and via in-home assistants such as Google Home to find answers to their every informational, navigational, and commercial need. And for each of those billions of queries, Google Search must find the right answer amongst the trillions of web pages in its index.
None of this would be possible without artificial intelligence (AI) and the scalability it creates. But how does Google AI impact local search? Let’s take a look.
What Is Google AI in Search?
Artificial intelligence is integral to the way search engines like Google function today. AI takes tasks that have historically required human energy and intelligence to complete and automates them. Its earliest applications were fairly simple automations but now, with machine learning, algorithms can be “trained” to make complex decisions, recognize speech, and more.
AI is used by search algorithms to understand the semantic meaning of each query, identify relevant results, and rank those in real-time in order to deliver the best answer.
Important AI Milestones for Google Search
In its earliest days, Google’s Search algorithm simply looked for words on the page to match words in a search query. However, this came with myriad issues; human language is complex, people express queries in all sorts of ways, and these systems were easy for people with less-than-honorable intentions to game. Even today, Google’s Pandu Nayak says that “15% of searches we see every day are entirely new.”
How do you teach a system to deliver results quickly for questions it’s never been asked before?
Enter AI.
It’s important to note that each Google Search experience is powered by potentially hundreds of algorithms. According to Nayak, Google Fellow and VP of Search, the search giant has developed hundreds of algorithms over the years to help deliver relevant search results.
“When we develop new AI systems, our legacy algorithms and systems don’t just get shelved away. In fact, Search runs on hundreds of algorithms and machine learning models, and we’re able to improve it when our systems — new and old — can play well together,” he explained. “Each algorithm and model has a specialized role, and they trigger at different times and in distinct combinations to help deliver the most helpful results.”
Here are some of the major AI applications running in Google Search and when they were added.
RankBrain, 2015
This was the first deep learning system Google AI deployed. RankBrain vastly improved Google’s understanding of how words translate into specific concepts by enabling it to find more information than it previously could and expanding the machine’s understanding of real-world ideas and connections. Nayak says that “RankBrain (as its name suggests) is used to help rank — or decide the best order for — top search results.”
Neural matching, 2018
Neural matching gave Google a better understanding of how queries relate to pages. This was a massive shift in how Google assessed queries and took it beyond keywords, to consider the query and content at scale, as opposed to just keywords. This would give both the query and content far greater context.
BERT, 2019
Bidirectional Encoder Representations, a Natural Language Processing model that revolutionized Google’s understanding of the meaning and intent of combinations of words. BERT considers every word in the query and can “understand” how different words used in tandem represent various concepts. “BERT understands words in a sequence and how they relate to each other, so it ensures we don’t drop important words from your query — no matter how small they are,” Nayak explained.
MUM, 2021
Google says its Multitask Unified Model is 1000 times more powerful than BERT. MUM is already trained across more than 75 languages and can complete many different tasks simultaneously. Sherry Bonelli of Early Bird Digital explains, “Instead of doing multiple searches for a complex question, MUM can multitask and will be able to find the answer to a complicated search query using multiple sources and mediums at the same time.” See Google’s MUM Update: What This Means For Local Marketers According to the Experts for more insights from SEOs.
Other Ways Google Uses AI
Google is using AI in numerous ways outside of Search, as well.
Google Assistant is one great example. You might already be using the AI-powered voice assistant at home, on your smartphone, in your car, on your TV, or even on a wearable such as a wristwatch. Using AI, this application can manage your calendar, find nearby businesses and even make appointments with them, check the weather, play music, and more.
Using machine learning and language models, Google Assistant can become increasingly better at understanding and delivering on your needs, as well.
Google also uses AI in Maps, whether historic location data and your search history are put to use in a more personalized navigational experience. AI is helping power Live View, giving Google Maps a better understanding of precisely where you are in relation to buildings and landmarks so it can better assist you in getting where you need to go.
Ai is being used by Google in:
- Its Android-based earthquake detection system
- For Smart Bidding in Google Ads and DoubleClick
- YouTube Safe Content recommendations
- Search for image recognition
- Google Drive smart scheduling based on the availability of contacts
- Google Translate, via the Google Neural Machine Translation network
- And more
How Will Google AI Be Used in the Future?
Jeff Dean, Senior Google Fellow, and SVP of Google Research, expects we’ll see a lot of exciting advances in machine learning in the years ahead.
“Researchers are training larger, more capable machine learning models than ever before. For example, just in the last couple of years models in the language domain have grown from billions of parameters trained on tens of billions of tokens of data (e.g., the 11B parameter T5 model), to hundreds of billions or trillions of parameters trained on trillions of tokens of data,” he wrote recently.
Many of these applications are focused on enhancing machines’ understanding of written language, he explained. Recent models have achieved “state-of-the-art results in language understanding benchmarks and open-ended conversational abilities, even across multiple tasks in a domain,” he said, and shared this example using Google’s LaMDA model for an open-ended conversation between a searcher and Google Search:
 |
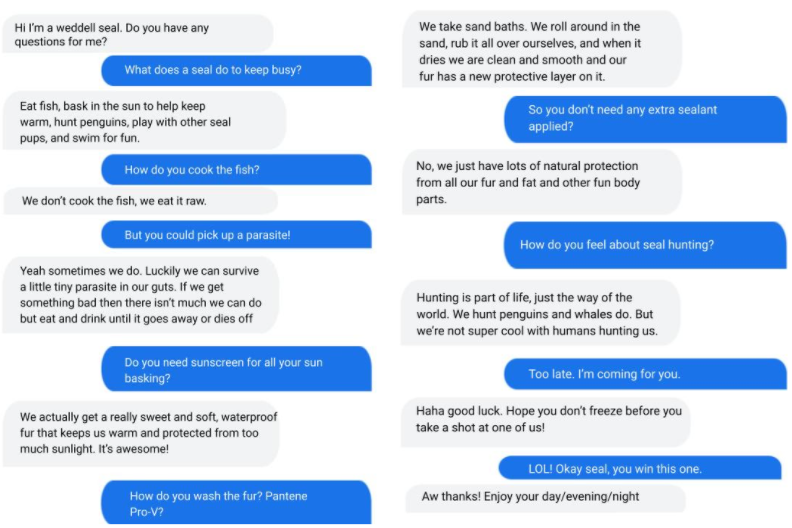
|
| A dialog with LaMDA mimicking a Weddell seal with the preset grounding prompt, “Hi I’m a weddell seal. Do you have any questions for me?” The model largely holds down a dialog in character. (Weddell Seal image cropped from Wikimedia CC-licensed image) |
Google AI FAQs
What’s so exciting about Google MUM?
Google MUM is multi-modal, meaning far more types and formats of content can be analyzed. Dean shared a few examples of what this means in his recent blog post, Google Research: Themes from 2021 and Beyond.
“These are some of the most advanced models to date because they can accept multiple different input modalities (e.g., language, images, speech, video) and, in some cases, produce different output modalities, for example, generating images from descriptive sentences or paragraphs, or describing the visual content of images in human languages.
What are some other examples of AI in action in Search?
Prabhakar Raghavan, Google’s SVP for Search & Assistant, shared a few more ways Google is using AI in an October 2020 blog post:
- To improve Google Search’s ability to understand misspelled words, as 1 in 10 search queries are misspelled.
- To better understand the relevancy of specific passages, which was expected to improve 7% of search queries across all languages.
- To apply neural nets that advance Google’s understanding of subtopics around an interest.
- To give searchers access to higher quality and more accurate information about the world around them.
- To better understand video content and identify key moments to highlight in Search results.
Where can I learn more about how Google uses AI?
These other resources may help deepen your understanding of Google’s use of AI:
- Google AI, the official blog
- How Google uses artificial intelligence In Google Search, Search Engine Land
- How AI is powering a more helpful Google, Prabhakar Raghavan
- Artificial Intelligence Powering Google Products, Towards Data Science
- AI and Machine Learning Products – Google Cloud
